How to Effectively Implement Collaborative Robots in Manufacturing Processes
The integration of collaborative robots in manufacturing processes is revolutionizing the industrial landscape. According to a report by the International Federation of Robotics, the adoption of collaborative robots, or cobots, in manufacturing has seen exponential growth, with a projected market increase of over 25% annually. This technological advancement not only streamlines operations but also enhances safety and productivity by allowing human workers to focus on higher-level tasks while robots manage repetitive functions.
Expert insights from Dr. Samantha Reynolds, a leading figure in robotics technology, emphasize the importance of strategically implementing these systems. She states, "The successful adoption of collaborative robots in manufacturing requires a deep understanding of both the technology and the processes it enhances." As manufacturers explore the potential of cobots, they must consider critical factors such as workforce training, integration challenges, and the alignment of robotic capabilities with production goals. This introduction sets the stage for a comprehensive examination of effective strategies for implementing collaborative robots in manufacturing, ensuring a seamless transition that maximizes the benefits of this groundbreaking technology.

Understanding Collaborative Robots and Their Role in Manufacturing
Collaborative robots, or cobots, represent a transformative advancement in the manufacturing landscape, facilitating a harmonious partnership between humans and machines. Unlike traditional industrial robots, which operate in isolation behind safety barriers, cobots are designed to work side by side with human workers, enhancing efficiency and safety. According to a report by the International Federation of Robotics, the global market for collaborative robots is expected to reach approximately $12 billion by 2025, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate of over 30%. This growth is driven by an increasing demand for automation in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which seek to improve production flexibility and maximize resource utilization.
Understanding the role of cobots in manufacturing is crucial for successful implementation. Cobots excel in repetitive and monotonous tasks, allowing human workers to focus on more complex activities that require creativity and critical thinking. A study conducted by McKinsey indicates that up to 45% of work activities can be automated using existing technologies, yet augmentation through cobots can lead to productivity increases of 30% in assembly lines. Furthermore, their user-friendly programming and adaptability mean that companies can integrate them without extensive training or downtime.
As manufacturing continues to evolve towards a more integrated and intelligent future, cobots stand at the forefront of this revolution, bridging the gap between human ingenuity and robotic precision.
Assessing the Impact of Collaborative Robots on Production Efficiency

The integration of collaborative robots, or cobots, in manufacturing processes has shown a significant positive impact on production efficiency. By working alongside human operators, these robots can automate repetitive and tedious tasks, thereby allowing workers to focus on more complex and value-added activities. This shift not only enhances overall productivity but also leads to a more satisfying work environment, as employees are relieved from monotonous labor and can engage in roles that require critical thinking and creativity.
Additionally, the adaptability of collaborative robots plays a vital role in improving efficiency. They can be easily programmed and reconfigured to handle various tasks within the production line, facilitating a seamless transition between different products or processes. This flexibility reduces downtime and accelerates production cycles, enabling manufacturers to respond quickly to market demands. Furthermore, the enhanced precision and consistency provided by cobots contribute to higher quality output, minimizing waste and increasing the overall yield of manufacturing processes. By assessing these impacts, companies can develop strategies that leverage collaborative robots effectively, ensuring that their implementation leads to sustainable improvements in efficiency and productivity.
Key Factors for Successful Integration of Robots into Manufacturing Systems
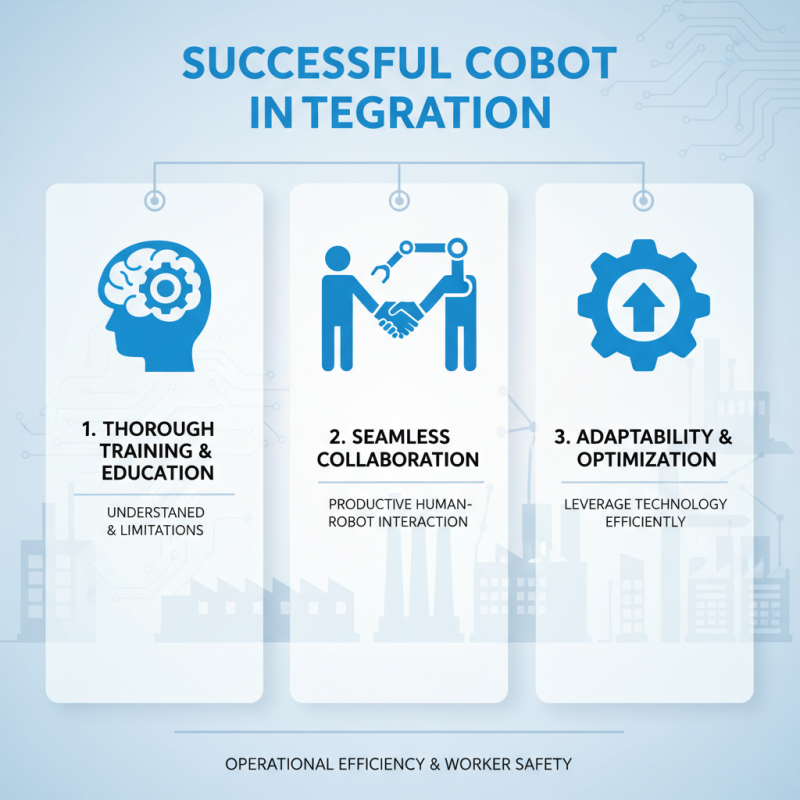
The successful integration of collaborative robots, or cobots, into manufacturing processes hinges on several key factors that facilitate both operational efficiency and worker safety. Firstly, thorough training and education of the workforce are crucial. Employees must understand how to work alongside cobots, comprehending their capabilities and limitations. This ensures that human-robot collaboration is seamless and productive, as well-informed workers can adapt to changes swiftly and leverage the technology optimally.
Secondly, the design and layout of the manufacturing environment play a significant role in the effective deployment of collaborative robots. Optimizing workflows to minimize bottlenecks and allowing sufficient space for cobots to operate freely can dramatically enhance productivity. Additionally, safety measures must be embedded into the design process; systems should be evaluated and adjusted to protect both human workers and robots, preventing accidents while fostering a collaborative atmosphere.
Lastly, continuous monitoring and evaluation of the implementation process are essential. This involves regularly assessing the performance of cobots and making data-driven adjustments to improve their integration. Feedback loops from employees can provide valuable insights into potential areas of improvement, ensuring that the collaborative robots are not only enhancing productivity but are also contributing to a safe and engaging workplace for all.
Training and Safety Considerations for Human-Robot Collaboration
When implementing collaborative robots (cobots) in manufacturing environments, training and safety considerations for human-robot collaboration are paramount. Effective training programs should encompass not only the technical skills required to operate and program the cobots, but also the importance of safety protocols. Workers must be educated on how to work alongside these robots safely, understanding the specific functionalities of the cobots, the potential risks involved, and the safety measures in place. Hands-on training sessions can enable employees to familiarize themselves with the robots’ movements, reinforce proper interaction techniques, and cultivate a culture of safety awareness.
Safety is a critical aspect of human-robot collaboration, requiring careful planning and implementation. It is essential to conduct a thorough risk assessment of the workspace to identify potential hazards. Safety features such as sensors, emergency stop functions, and physical barriers can significantly mitigate risks. Moreover, regular safety audits and continuous monitoring of the robots’ operations can help ensure compliance with safety standards and regulations. By fostering an environment where both workers and robots can coexist safely and efficiently, organizations can enhance productivity and ensure that all personnel feel secure and confident in their collaborative roles.
Measuring Return on Investment: Benefits of Implementing Collaborative Robots
Implementing collaborative robots (cobots) in manufacturing processes offers numerous benefits that can significantly enhance productivity and efficiency. One of the most crucial aspects to consider is the return on investment (ROI). By automating repetitive tasks, cobots allow human workers to focus on higher-value activities, resulting in a more efficient allocation of labor resources. This shift not only increases overall productivity but also leads to greater employee satisfaction, as workers can engage in more challenging and rewarding jobs.
Measuring the ROI of collaborative robots can be achieved through various metrics, such as increased output, reduced labor costs, and minimized error rates. For instance, organizations can track production rates before and after cobot implementation to quantify the direct impact on output. Furthermore, cobots' ability to operate alongside human workers without safety concerns helps reduce downtime and enhances overall operational flexibility. By analyzing these metrics, manufacturers can create a clear picture of the benefits gained from integrating cobots into their processes, ultimately justifying the initial investment and paving the way for future advancements.
How to Effectively Implement Collaborative Robots in Manufacturing Processes - Measuring Return on Investment: Benefits of Implementing Collaborative Robots
| Metrics | Before Implementation | After Implementation | Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Production Time (hrs/week) | 40 | 30 | -25% |
| Labor Costs (per week) | $3000 | $2000 | -33.3% |
| Defect Rate (%) | 5% | 2% | -60% |
| Overall Equipment Effectiveness (%) | 70% | 85% | +21.4% |
| Return on Investment (%) | N/A | 150% | N/A |
Related Posts
-

Unlocking Efficiency: How Collaborative Robots are Transforming Modern Industries
-
Unlocking the Future of Work with Robotics and Automation Trends and Innovations in 2023
-

What is Robotics and Automation Driving the Future of Industry with 25 Percent Growth by 2025
-

Exploring the Future: How Robotics Software is Transforming Modern Industries
-

How to Leverage Robotic Automation Solutions for Streamlined Business Processes
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Cobot Robots in Modern Manufacturing
